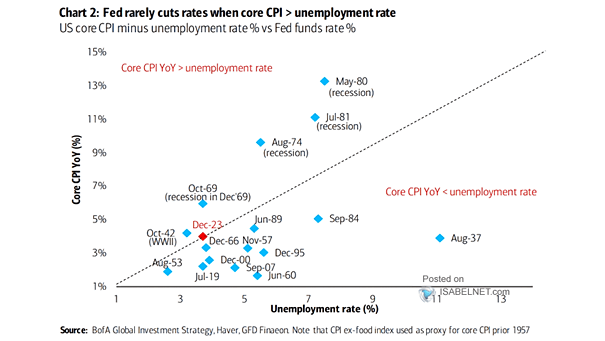
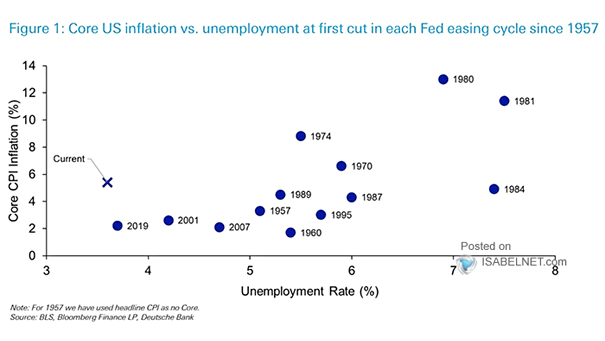
U.S. Core CPI Minus Unemployement Rate % vs. Fed Funds Rate
U.S. Core CPI Minus Unemployement Rate % vs. Fed Funds Rate The Fed rarely cuts rates when core CPI exceeds the unemployment rate, reflecting the central bank’s concern about potential inflationary pressures in the economy and its emphasis on price stability. Image: BofA Global Investment Strategy